Here you can find the detailed instruction on how to export data from any database to Oracle database in Exportizer software.
Below, it is shown how to export data from GUI or command line.
Export Conditions
In most cases, to export data to Oracle, it is important to fulfill the following conditions:
- We recommend to use Exportizer Enterprise and FD interface when working with Oracle databases. FD engine does not require ODBC drivers and exports data much faster. But if you prefer to use ODBC for both (source and target) databases, Exportizer Pro can be used.
- Oracle client must be installed. Make sure the Exportizer and Oracle client have the same architecture, i.e. either all are 32-bit or all are 64-bit.
- All other involved components, i.e. Exportizer, ODBC drivers (if you use ODBC on source or target side), OLE DB providers etc., should have the same architecture: 32-bit or 64-bit.
Note: If your operating system is 64-bit, you can install both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the Exportizer software and use them independently.
Export to Oracle Preparations
If you are exporting data via GUI:
- Launch Exportizer Pro or Exportizer Enterprise.
- Register your source database.
- Register your target Oracle database. You can register it by several ways. Note: You can register the target database from the Export dialog during the exporting.
Export Steps (GUI)
- Open the registered source database.
- Choose a dataset or datasets to export:
- select a table from the table list;
or - open an SQL window, then write and execute an SQL query;
or - select multiple tables in the table list; before doing that, click Select Tables button
 ;
;
or - prepare a mix of multiple tables and/or SQL queries: open multiple tables one by one and multiple SQL windows; in SQL windows, write your database queries and execute them to get the result sets.
Please note that exporting multiple datasets at a time is available in Exportizer Enterprise only.
- select a table from the table list;
- Click Export button
 or choose a needed item from Export menu.
or choose a needed item from Export menu. - Switch to the Database tab and select your registered Oracle database as a target database. If you did not register it yet, click '...' button to the right to register it.
- Specify export parameters. Some notes:
- Turn on the Memory saving mode option and its related options. In case of exporting problems, if you suspect that they can be caused by these options, try different combinations of them. If exported data or column names on any side can contain Unicode characters, set the corresponding stream Encoding, e.g. UTF-8.
- Specify the Table name, i.e. name of the target table. For multi-table exporting, you can leave it empty, otherwise, the data will be exported to one destination table; anyway, the source-to-target table mappings are available at the next step.
- Optionally, specify the target table description (comment). For multi-table exporting, leave it empty; you will be able to specify the target descriptions later on the Table Mappings step.
- Choose the Export mode. Some modes allow you to update data in existing table(s), some modes can create destination tables, etc. To learn about all possible modes, read detailed description for Database export format. For multi-table exporting, this mode will be applied to the most of the tables, and you can override it for specific tables at the next step. For example, it can be Replace+Insert for the most of tables, and Update or Append+Update or even DELETE for others etc.
- The bigger Commit interval value, the faster your exporting process. But too big value may cause memory and other issues. Therefore, try to play with it to find the optimal value before porting the solution to your production environment.
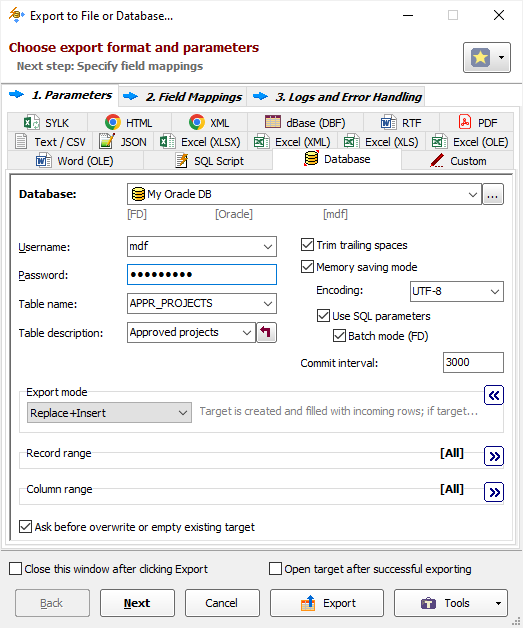
- Click Next.
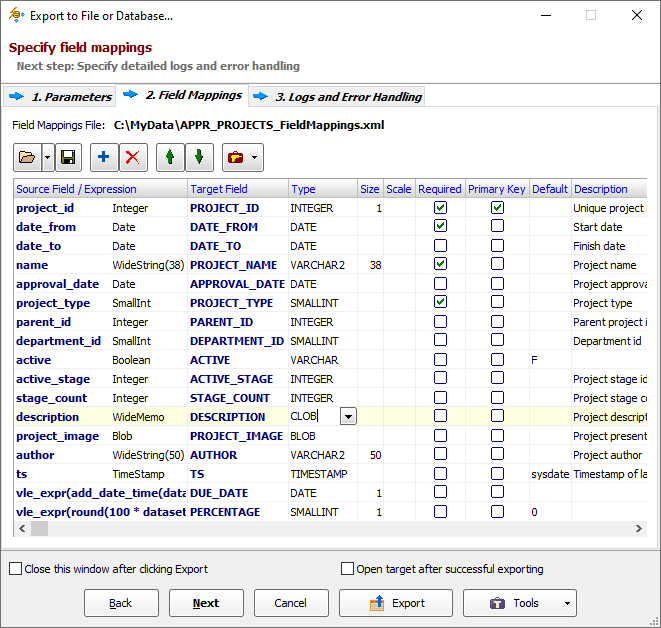
For multi-table exporting, specify the source-to-target table mappings, otherwise check the source-to-target field mappings.
In field mappings, you create the correspondence between the source and target columns.
In field mappings, in addition to source table fields, you can also use calculated fields specified by formulas.
It is possible to define full specifications for target columns here, i.e. rename target columns, choose their types, specify NOT NULL constraints, default values, primary key flags, descriptions (comments) etc. These specifications will be applied when the target table needs to be created or overwritten.
In table mappings (for multi-dataset exporting), you create the correspondence between the source datasets (tables and/or queries) and target tables. Here, you can specify target table names, their descriptions (comments), and nested field mappings for each table pair.
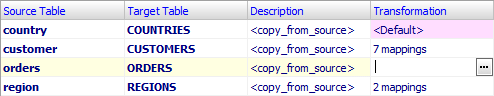
You can skip this step by clicking Export instead of clicking Next. In this case table and/or field mappings will be built automatically, which may be not desirable.
- Click Next to proceed to export logs and error handling options or click Export to start the export process immediately.
Resolving Export Performance Issues
In the case of the slow performance, there are some actions you can try:
- First of all, make sure the target database is connected via FD interface. Using FD on the target side lets you utilize batch SQL commands execution which can speed up the exporting process drastically.
- Try different combinations of Memory saving mode options and Commit interval setting. It is recommended to turn on the Memory saving mode, Use SQL parameters and Batch mode options and set the value of Commit interval from several hundreds to several thousands depending on you target server resources.
- Finally, you might want to read all the data exporting recommendations.
Exporting Data to Oracle from Command Line
When you export data from the command line, you do not need to register the source and target databases (but you still can). Please note that using registered databases allows you to shorten the command line and to hide the database passwords; another option to hide the passwords is to use OS authentication (see example below).
In examples below, we do not use registered databases. Parameter /TrgDB is the name of your destination Oracle database from the tnsnames.ora file.
Command Line Examples
Exporting a DBF table to Oracle using OS authentication:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /CommitInterval=1000 /TrimTrailingSpaces /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /FieldMappings=ID=ID;CUSTID=CUSTOMER_ID;SALEDATE=SALE_DATE;TOTALSUM=TOTAL_SUM;TAXRATE=TAX_RATE;INVOICE=INVOICE /SrcDBInterface=ADO /SrcDBKind=DSN /SrcDBDriver=DBASE /SrcDB=rptizer /SrcTableName=orders.dbf /TrgDBInterface=FD /TrgDBKind=DSN /TrgDBDriver=ORACLE /TrgOSAuthentication=Yes /TrgAuthenticationMode=Normal /TrgVendorHomepath=C:\app\John\product\12.1.0\client_1 /TrgDB=cloud_prod /TrgTableName=ORDERSConverting data from several SQLite tables to Oracle in silent mode:
exptizer.exe /silent /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /IncludeMemo /CommitInterval=500 /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLite /SrcDB=C:\TEST\employees.db /TrgDBInterface=FD /TrgDBKind=DSN /TrgDBDriver=Oracle /TrgOSAuthentication=Yes /TrgAuthenticationMode=Normal /TrgCharset=UTF8 /TrgVendorHomepath=C:\app\John\product\12.1.0\client_1 /TrgDB=cloud_prod "/TableMappingsFile=c:\DWH\Export\SQLite-To-Oracle-Table-Mappings.xml" /LogFile=C:\DWH\Export\Log\export.log /AppendLogThe table mappings file (/TableMappingsFile parameter) must be prepared before the exporting. It must contain the source-to-target table mappings. It can be prepared in GUI Export dialog or manually using the documentation.
Exporting multiple PostgreSQL tables to Oracle in silent mode:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /silent /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /IncludeMemo /CommitInterval=800 /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=DSN /SrcDBDriver=POSTGRESQL "/SrcServer=222.333.2.14" /SrcPort=5432 /SrcDB=dwh /SrcDBUserName=dwh_master /SrcDBPassword=dwh_master_password /TrgDBInterface=FD /TrgDBKind=DSN /TrgDBDriver=ORACLE /TrgOSAuthentication=Yes /TrgAuthenticationMode=Normal /TrgVendorHomepath=C:\app\John\product\12.1.0\client_1 /TrgDB=cloud_prod "/TableMappingsFile=c:\DWH\Export\PostgreSQL-To-Oracle-Table-Mappings.xml" /LogFile=C:\DWH\Export\Log\export.log /AppendLogNote: You can add other parameters to the command lines above in accordance with the documentation.
Action File Example
The last command line can be transformed to an action file, which is much more comfortable to work with. You can run action files either form the command line or from Exportizer GUI. The action file contains all the command line parameters (except /silent switch), one parameter per line, and allows comments:
/export
/ExportType=DATABASE
/ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT ;Target tables recreated when exist
;/ExportMode=APPEND ;Incoming records are appended to target tables
/MemorySaving
/UseSQLParameters
/UseBatchMode
/Encoding=UTF-8
/CommitInterval=400 ;COMMIT after exporting every 400 records
/SrcDBInterface=FD
/SrcDBKind=DSN
/SrcDBDriver=POSTGRESQL
/SrcServer=222.333.2.14 ;IP address or server URL
/SrcPort=5432
/SrcDB=dwh
/SrcDBUserName=dwh_master
/SrcDBPassword=dwh_master_password
/TrgDBInterface=FD
/TrgDBKind=DSN
/TrgDBDriver=ORACLE
/TrgOSAuthentication=Yes
/TrgAuthenticationMode=Normal
/TrgVendorHomepath=C:\app\John\product\12.1.0\client_1
/TrgDB=cloud_prod ;a name from tnsnames.ora file
/TableMappingsFile=c:\DWH\Export\PostgreSQL-To-Oracle-Table-Mappings.xml ;a file with table source-to-target table mappings
/LogFile=C:\DWH\Export\Log\export.log ;a file for writing logs to
/AppendLog ;keep previous logs and add new logs to the end of the log fileSee also



