Here you can find the detailed instruction on how to convert data from different database types to Microsoft Excel in Exportizer software.
Below, it is shown how to export data directly (from GUI or command line), or using clipboard.
Note: Exportizer also provides the ability to export data to intermediate file formats. For example, you can export data to CSV or DBF format, and then open the destination .csv or .dbf file in Excel: it is faster, but has some inconveniences comparing with direct exporting to Excel (e.g. when exporting multiple tables to different sheets of one Excel workbook). Exporting to intermediate file formats is not covered in this topic.
Export Conditions
In most cases, to export data to Microsoft Excel, it is important to fulfill the following conditions:
- It is important to choose the proper Excel output format:
- When exporting to Excel (OLE) target format, Microsoft Office must be installed; Exportizer and Microsoft Office should be both 32-bit or both 64-bit.
- When exporting to other Excel formats like XLS or XLSX, Microsoft Office is not required, and you can use either Exportizer 32-bit or Exportizer 64-bit.
Note: If your operating system is 64-bit, you can install both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the Exportizer software and use them independently.
Export Steps (GUI)
- Launch Exportizer.
- Register and open your source database.
- Choose a dataset or datasets to export:
- select a table from the table list;
or - open an SQL window, then write and execute an SQL query;
or - select multiple tables in the table list; before doing that, click Select Tables button
 ;
;
or - prepare a mix of multiple tables and/or SQL queries: open multiple tables one by one and multiple SQL windows; in SQL windows, write your database queries and execute them to get the result sets.
Please note that exporting multiple datasets at a time is available in Exportizer Enterprise only.
- select a table from the table list;
- If your case is a, b, or c, proceed by clicking Export button
 . Otherwise, choose Export | Export Open Datasets... menu.
. Otherwise, choose Export | Export Open Datasets... menu. - Choose the target Excel format. You have several formats available:
- Excel (XLS). The fastest. Limited to 65535 rows (but there are some workarounds). Does not support data formatting yet.
- Excel (XLSX). The most configurable. The speed is moderate. Allows multiple tables to be written to different sheets of one target file.
- Excel (OLE). The slowest. Requires Microsoft Office installed.
- Excel (XML-based). Fast. For backward compatibility.
Please note that adding data to an existing Excel file is not supported yet.
- Specify a target file (for multi-table exporting, you can specify a folder, where the target files will be created) and needed export parameters.
Note: If you later need to open the target Excel file in a database tool like Exportizer, make sure to specify the range name for the output table; named ranges are seen as separate tables when opening Excel file by most Excel ODBC drivers.
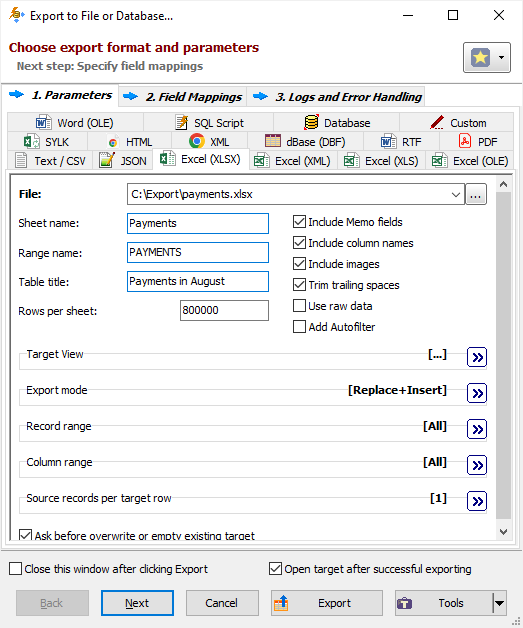
In the Target View block, you can customize how the data inside Excel sheet will look like. If you turn on Use GUI settings option there, the target will look similar to what you see in Exportizer data grid; but this option will be ignored if you running the export operation from the command line in silent mode, because there is no GUI in the silent mode.
In the Source records per target row block, you can specify how many source records to put in one target Excel row. For example, if you specify 2, the data will be exported in two major target columns, where the first of them will contain the odd records of the source, and the second major column will contain the even records of the source. It can be useful if your source database has a small number of columns.
- Click Next.
Specify the source-to-target table and/or field mappings.
In field mappings, you create the correspondence between the source and target columns. In addition to source table columns, you can also use calculated fields specified by formulas.
In table mappings (for multi-dataset exporting), you create the correspondence between the source datasets (tables and/or queries) and target Excel files. If you export to Excel (XLSX) format, you can specify a different sheet name and table title for each exported dataset. You can also specify nested field mappings for each table pair.
- Click Next to proceed to export logs and error handling options or click Export to start the export process immediately.
Resolving Export Performance Issues
In the case of the slow exporting, the actions you can try depend on used Excel export format:
- Excel (OLE). Please read important notes about this format. Try another export format.
- Excel (XML-based). This format is mainly for backward compatibility. Try another export format.
- Excel (XLS). This is the fastest format. There are quite a few chances for its speed improving. One thing that can be done is to ensure the data source is fast:
- Try to use SQL queries wherever possible.
- If the data source is not to big, try fetch all rows before the exporting. To do this, click Last Record button.
- Excel (XLSX). First, try to optimize the data source (see above) to make sure the problem is something else. Next, consider the data exporting recommendations.
Exporting Data to Excel Using Command Line
- Exporting a table from SQLite file to XLSX file:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=EXCELXLSX /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /RowsPerSheet=800000 /SheetName=Employees "/TableTitle=Company Employees" /RangeName=employee /IncludeColNames /IncludeImages /IncludeMemo /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE /SrcDB=C:\MyData\org.db /SrcTableName=employee /TrgDB=C:\TEST\employee.xlsx - Exporting all tables from SQLite file to Excel files (one table per Excel file):
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=EXCELXLSX /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /RowsPerSheet=800000 /IncludeColNames /IncludeImages /IncludeMemo /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE /SrcDB=C:\MyData\org.db /SrcTableName=* /TrgDB=C:\TEST\*.xlsx - Exporting several tables from SQLite file to one target XLSX file (one table per Excel sheet):
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=EXCELXLSX /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /RowsPerSheet=800000 /IncludeColNames /IncludeImages /IncludeMemo /TableMappingsFile=C:\TEST\Sqlite2ExcelTableMappings.xml /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE /SrcDB=C:\MyData\org.db /TrgDB=C:\TEST\ - In the last case, please pay attention to how the source-to-target table mappings are defined. We use /TableMappingsFile parameter which points to an XML file with the mappings definition. For exporting three tables, the file content may look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <TableMappings> <Items> <TableMapping> <Source> <TableName>employee</TableName> </Source> <Target> <FileName>org.xlsx</FileName> <TableTitle>Company Employees</TableTitle> <SheetName>Employees</SheetName> <RangeName>employee</RangeName> </Target> </TableMapping> <TableMapping> <Source> <TableName>goods</TableName> </Source> <Target> <FileName>org.xlsx</FileName> <TableTitle>Available Goods</TableTitle> <SheetName>Goods</SheetName> <RangeName>goods</RangeName> </Target> </TableMapping> <TableMapping> <Source> <TableName>salary</TableName> </Source> <Target> <FileName>org.xlsx</FileName> <TableTitle>Position Salaries By Department</TableTitle> <SheetName>Salaries</SheetName> <RangeName>salary</RangeName> </Target> </TableMapping> </Items> </TableMappings> - The last command line above can be transformed to an action file:
/export /ExportType=EXCELXLSX /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT ;Target files will be overwritten if they exist /TableMappingsFile=C:\TEST\Sqlite2ExcelTableMappings.xml /RowsPerSheet=800000 /IncludeColNames /IncludeImages /IncludeMemo /SrcDBInterface=fd /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE /SrcDB=C:\MyData\org.db /TrgDB=C:\TEST\If you save this text, for example, to C:\MyData\ExportAction_SQLite2Excel.txt, then your command line will look like:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /silent /ActionFile=C:\MyData\ExportAction_SQLite2Excel.txt - Exporting a table from PostgreSQL database to Excel file:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=EXCELXLSX /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /RowsPerSheet=800000 /SheetName=Employees "/TableTitle=Company Employees" /RangeName=employee /IncludeColNames /IncludeImages /IncludeMemo /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=DSN /SrcDBDriver=POSTGRESQL "/SrcServer=222.333.2.14" /SrcPort=5432 /SrcDB=dwh /SrcDBUserName=dwh_master /SrcDBPassword=dwh_master_password /SrcTableName=employee /TrgDB=C:\TEST\employee.xlsx - Exporting a table from Interbase database to XLSX file:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=EXCELXLSX /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /RowsPerSheet=800000 /IncludeColNames /IncludeImages /IncludeMemo /AddAutofilter /TrimTrailingSpaces /FieldMappings=ID=ID;FIRSTNAME=FIRSTNAME;LASTNAME=LASTNAME;CITY=CITY;COUNTRY=COUNTRY /SrcDBInterface=FD /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=INTERBASE /SrcDB=C:\MyData\TEST.GDB /SrcOSAuthentication=No "/SrcVendorLibrary=C:\Program Files (x86)\Embarcadero\Studio\15.0\InterBaseXE3\bin\gds32.dll" /SrcTableName=CUSTOMER /TrgDB=C:\MyData\customer.xlsx
Exporting Data Using Clipboard
- Launch Exportizer.
- Register and open your source database.
- Open the source table or write and execute your SQL query.
- Copy the needed data. You can do this in two ways:
- Quick, but limited. Select a range of cells in a visible part of the data grid, then click Ctrl+C.

- Flexible. Click Copy Data button
 . Choose Text/CSV format, Standard schema, Tab field separator, and specify other options if needed. Then click Copy.
. Choose Text/CSV format, Standard schema, Tab field separator, and specify other options if needed. Then click Copy.
- Quick, but limited. Select a range of cells in a visible part of the data grid, then click Ctrl+C.
- Launch Microsoft Excel and paste the copied data to its sheet.
See also



