You can SQLite databases in Exportizer using these ways:
1. Opening through FD interface. Select FD interface, click SQLite, then fill all needed database parameters.
Database connection parameters:
(required parameters are highlighted)
| Parameter | Description | Value example |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor library | A path to installed SQLite library (when the application cannot find it automatically) | C:\sqlite\sqlite3.dll |
| Database | A path to a database. A path can include path variables. Instead of real database, you can specify ':memory:' to work with an empty in-memory database. | c:\databases\products.db |
| Shared cache | Enables or disables SQLite shared cache. | True |
| Blocking mode | Sets the database connection locking mode. Possible values:
| Exclusive |
| Open mode | Sets the database open mode. Possible values:
| ReadWrite |
| String format | Defines text data representation. Possible values:
| Unicode |
| GUID format | Defines the way of storing GUID values. Possible values:
| String |
| Date and time format | Defines the way of storing date and time values. Possible values:
| String |
| Synchronization mode | Sets the database connection synchronization mode of the in-memory cache with the database. Possible values:
| Off |
| Foreign keys | Enables foreign key usage (if SQLite version is 3.6.19 or above). Possible values:
| On |
| Extensions | Enables or disables loading SQLite extensions. | False |
| SQLite advanced | Additional SQLite database connection options. See SQLite documentation for supported Pragma statements. | |
| Password | Specifies password for encrypted SQLite database. | |
| SQL command separator | Specifies a separator for SQL commands in multi-command SQL scripts. | ; |
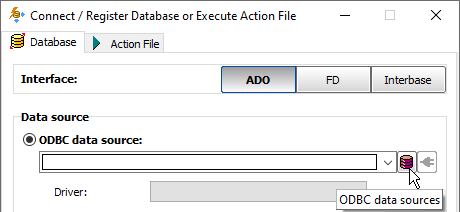
2. Opening through ODBC DSN. Create (if it does not exist yet) an ODBC DSN of the corresponding type using Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator, and point it to your database file. Then select ADO or BDE interface, choose ODBC data source option and then select the needed ODBC DSN from the drop-down list.
3. Opening through connection string (interface: ADO). Select Connection string option and write a connection string. This way is the most flexible one because it allows to specify many additional parameters in the connection string and override standard Exportizer connection behavior. But it is recommended basically for advanced users. Here are basic connection strings (more examples and details can be found in the Internet):
Driver=SQLite3 ODBC Driver;Database=C:\MyData\My_db.db; (SQLite3 ODBC Driver must be installed)
Attention
- This database type is supported only in Exportizer Enterprise and Exportizer Pro (the latter one can open such databases via ODBC only).
- The bit-version (32 or 64) of SQLite vendor library must match the bit-version of the application.
- When choosing the ODBC option, please make sure the corresponding ODBC driver installed and the bit-version of it matches the bit-version of the application (32 or 64).
Notes
- Each Exportizer edition has both 32-bit and 64-bit versions. You can install both and use them depending on what type of database you need to work with.
- You can invoke the ODBC Data Source Administrator directly from Exportizer when it was launched in administrator mode:
See also



